3D Printer Drive System Overview

Drive system overview
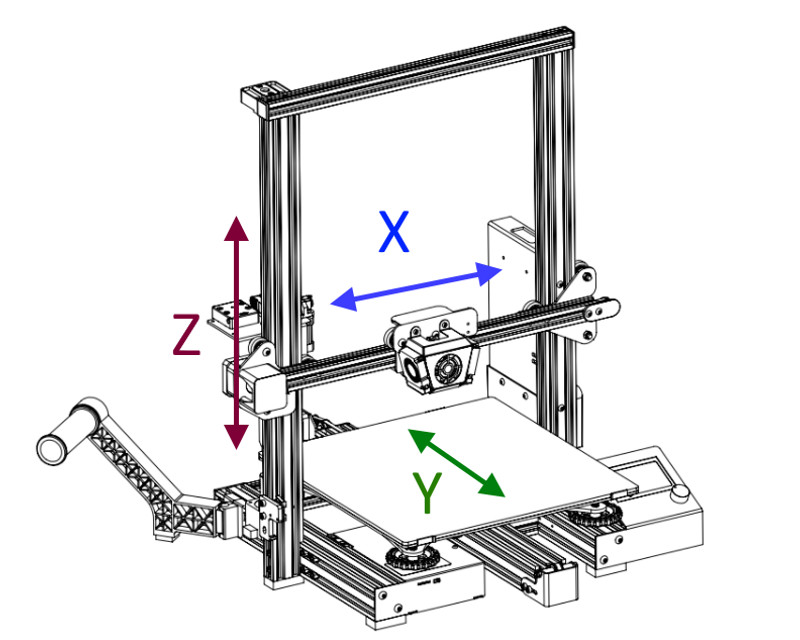
The drive system, or motion system, is an important component of filament 3D printers since it controls the movement of the print head in all 3 dimensions. It translates digital instructions into physical movement, controlling the precise positioning of the print head along the X, Y, and Z axes.
In an FDM 3D printer, the object being printed is created layer by layer, and the printer must precisely control the position of the print head to ensure that each layer is deposited correctly. The drive system moves the print head around the build area in the horizontal (X and Y) and vertical (Z) axes. The accuracy of these movements directly impact the quality of the 3D printed object. The drive system must balance speed and quick acceleration aginst precision.
The type of drive system singificantly impacts the printer’s top speed, noise levels, and overall print quality. There are different ways to build a drive system, each offering different balances between speed, accuracy, complexity, and reliability. They each have their own unique benefits and drawbacks, which can make them more suitable for certain applications than others. The drive system also often affects the overall size of the 3D printer, with some drive systems significantly adding to the bulk of a machine.
It’s important to know the different options available so you can make sure to choose a 3D printer with a drive system that most closely matches your needs.
How the drive system works
All drive systems use a collection of stepper motors to guide the extruder’s path along the X (left to right), Y (front to back), and Z (up and down) axes. Motors are linked to the print head using a combination of belts, linear rails, or lead screws, and are controlled by the 3D printer’s mainboard. Stepper motors are ideal for printer motion since they make precise, incremental movements. These movements are transformed into linear motion along the corresponding axis using a belt or leadscrew.
By manipulating the extruder’s position in three dimensions with high precision, the drive system enables the 3D printer to deposit filament exactly where it’s needed, building up the object layer by layer.
Let’s take a look at the most common types of drive systems on the market.
Drive System Types
There are several types of XYZ drive systems commonly used in FDM 3D printers. There are a few rare types we have not mentioned, but the most common are:
- Standard Cartesian: This is the most straightforward and common type of XYZ drive system. Each axis operates independently of the others, with a dedicated motor controlling movement along that axis.
- H-Bot: In an H-Bot system, movement in the X and Y axes is controlled by two motors working in tandem, while a third motor controls the Z-axis. This design allows for faster and smoother movement, but it can be more complex to set up and calibrate.
- CoreXY: Like the H-Bot, the CoreXY system uses two motors to control movement in the X and Y axes. However, it employs a unique belt configuration that can provide faster speeds and higher precision than the H-Bot or Standard Cartesian systems, although it’s also more complex.
- Delta: The Delta system is a unique motion system where three vertically oriented stepper motors control the movement of the print head across all three axes in unison. This results in a highly precise and quick motion but comes with increased complexity in setup, calibration, and maintenance.
Each of these systems offers different advantages and trade-offs in terms of speed, accuracy, complexity, and reliability. Let’s take a closer look at each of these drive systems.
Standard Cartesian Drive System
In a Standard Cartesian system, there are three stepper motors, each dedicated to an individual axis. The motors are attached to either lead screws or belts, which convert the rotational movement of the motor into linear motion along the corresponding axis. Linear guides or rails are incorporated into the system to ensure the smooth, straight movement of the print head.
One key characteristic of the Standard Cartesian drive system in 3D printers is the movement of the print bed along the Y-axis. These printer types are sometimes referred to as “bedslingers” for this reason. The moving bed requires more clearance around the front and back of the printer to accommodate the movement of the bed. However, this feature can also introduce challenges. For larger prints, the moving bed can impact the overall quality of the print due to potential instability or vibration. Additionally, the moving bed design can constrain the printer’s operating speed, as higher speeds may lead to a loss of accuracy.
Despite these potential limitations, the Standard Cartesian system typically comes at a lower cost due to its simpler design and fewer components. The independent control of each axis allows for easy calibration and maintenance, making it a user-friendly choice for beginners or hobbyists. It’s also suited for applications where speed limitations are not a concern, and where reliability and ease of maintenance are important considerations. However, tasks requiring higher speed or precision might benefit more from other drive systems.
H-Bot Drive System
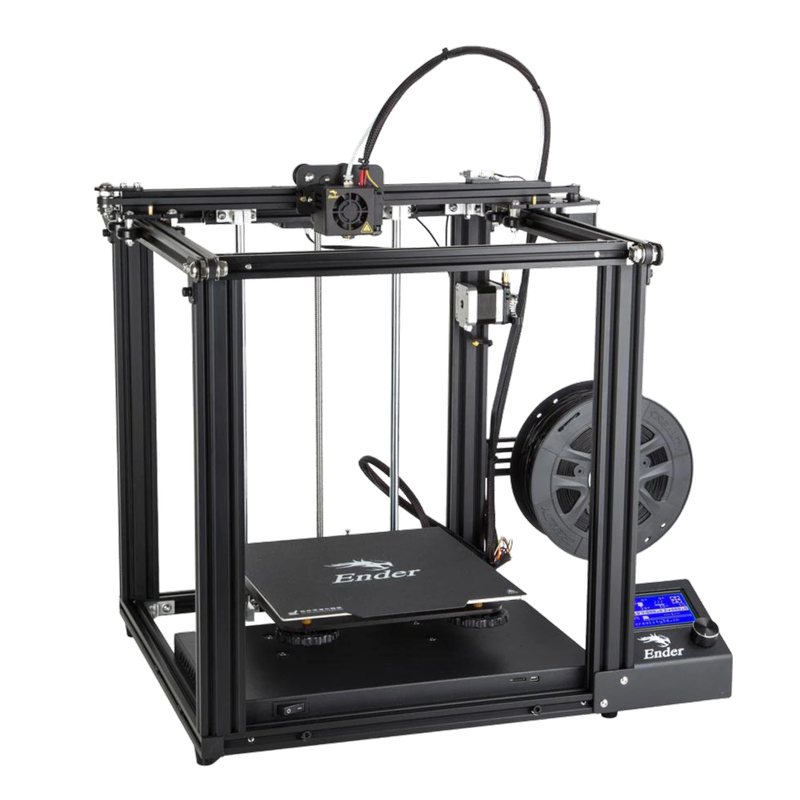

Like a Cartesian printer, the Extruder moves along a rod in the X axis. However, the Y axis motion is achieved by moving the entire print head, supporting rod, and drive motor in the Y direction, instead of moving the bed. This arrangement forms an “H” shape, hence the name “H-Bot”. This design enables faster and smoother movements compared to the Standard Cartesian system since it is not moving the heavy bed and printed parts. A separate motor controls the vertical movement of the print bed along the Z axis.
The defining characteristic of the H-Bot drive system is that the print bed moves only vertically, along the Z-axis. This static XY positioning allows for a more stable printing platform, reducing the potential for wobble or vibration that could impact the print’s quality. Additionally, with only the print bed moving vertically, there’s no need for additional clearance on the sides of the printer, making it more compact compared to Standard Cartesian printers.
While the H-Bot system is generally more expensive than the Standard Cartesian system due to its complexity and additional components, it offers distinct advantages for certain use cases. It’s particularly well-suited for applications requiring high precision and speed, and for situations where a more compact printer footprint is desired. However, for beginners or for applications that prioritize simplicity and ease of maintenance, the Standard Cartesian system might still be a more suitable choice.
CoreXY Drive System
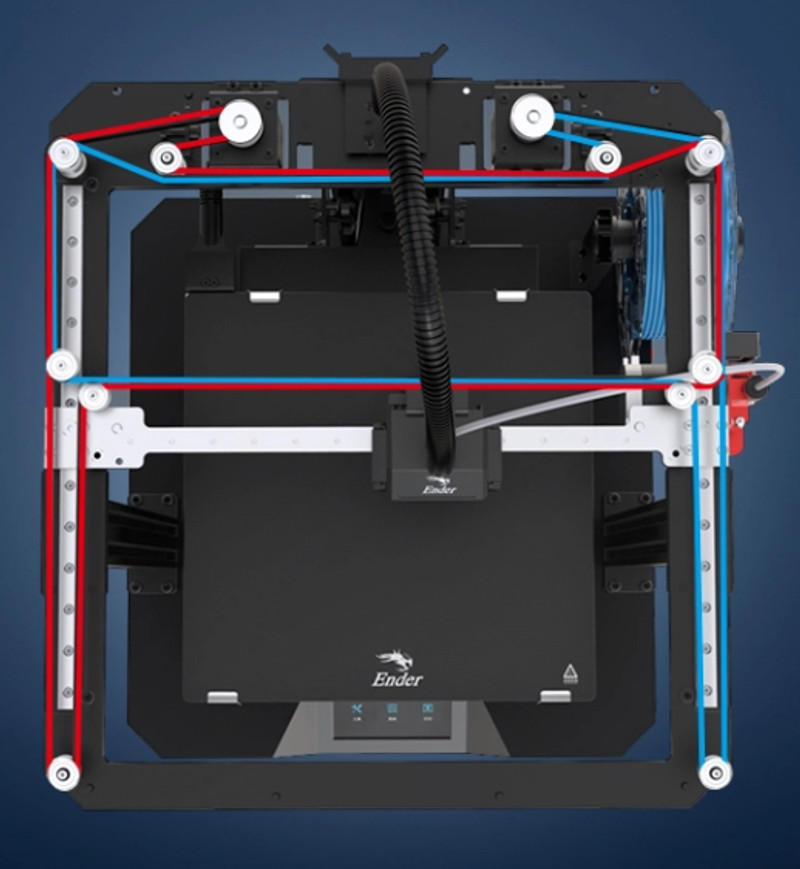

The CoreXY drive system is a more sophisticated type of motion system, designed to offer higher speed and precision compared to both the Standard Cartesian and H-Bot systems. Like the H-Bot system, the CoreXY system uses two motors to control movement along the X and Y axes. However, it utilizes a unique belt configuration that allows for faster printing speeds.
In a CoreXY system, the two stepper motors are mechanically interconnected through a complex arrangement of belts. This configuration allows both motors to contribute to movement along both the X and Y axes while both remaining stationary, resulting in less weight being moved and therefore faster and more precise motion. Like the H-bot, a separate motor controls the vertical movement of the print bed along the Z axis.
Despite the faster speed, the CoreXY system’s intricate belt configuration makes it more complex to assemble, calibrate, and maintain. It may also be more prone to mechanical issues over time due to the increased number of moving parts. Also, the cost of a CoreXY system is generally higher than that of standard Cartesian or H-Bot systems due to its complexity and additional components.
The CoreXY drive system is ideal for applications that require high speed and high precision. However, its complexity can make it less suitable for beginners or if simplicity and ease of maintenance are more important than speed.
Delta drive system

The Delta drive system is a unique and innovative motion system utilized in FDM 3D printers. Named after its resemblance to the Greek letter Delta, this system has significant differences from Cartesian-based systems like Standard Cartesian, H-Bot, and CoreXY.
In a Delta system, the movement of the print head along the X, Y, and Z axes is controlled by three vertically oriented stepper motors. These motors work in unison to manipulate a set of articulated arms, to which the print head is attached. The distinctive feature of this system is that all three motors contribute to the motion on all three axes. This means the print head’s position is the result of the combined movement of all three motors.
However, the complex motion kinematics of a Delta system make it more challenging to set up, calibrate, and maintain. As it uses a circular print bed, it can also be less intuitive to work with compared to the rectangular print beds of Cartesian-based systems. Despite its complexity, the Delta system can offer a high degree of precision and speed, offering similar benefits as the Core-XY configuration
Due to their complexity and the high degree of precision they offer, Delta systems tend to be more expensive than Standard Cartesian or H-Bot systems. They are also typically more limited in build volume, and have become less common in the marketplace.
Final Thoughts
The type of drive system used in FDM 3D printers primarily impacts the cost, speed, and print quality. Each system - Standard Cartesian, H-Bot, CoreXY, and Delta - has unique characteristics that offer particular advantages and drawbacks.
If you are just getting started with 3D printing or on a budget, a Standard Cartesian printer is a good choice since you likely will not need to push the limits of speed when you are learning. If speed is a bigger factor or if you have limited space, an H-bot or even CoreXY may be worth the extra cost and complexity.